Since the announcement of AMD’s Zen 3 core microarchitecture, we’ve been expecting three series of products to be announced: desktop Ryzen, mobile Ryzen, and enterprise EPYC. So far the desktop parts are now launched and at retail (if you can find them), and the mobile Ryzen processors are part of AMD’s CES disclosures this week for retail in February. That only leaves Zen 3-based EPYC, which AMD has decided to preview as part of its CES keynote presentation today.
As far as the design of Zen 3 EPYC ‘Milan’ processors go, we are expecting an almost seemless transition from the previous Zen 2 EPYC ‘Rome’ ecosystem, with pin-compatible processors offering up to 64 cores and with 128 PCIe 4.0 lanes. For performance, if the desktop processors are anything to go by, we should expect to see +19% IPC gains as well. The question remains as to frequencies and efficiency, and when the time comes for AMD to announce the product stack, we will see where the solution lies relative to the competition – should AMD have a significant competitive advantage, no doubt prices will rise in line as well. The previous generation EPYC 7742 had a ‘list price’ of $6950 for comparison.
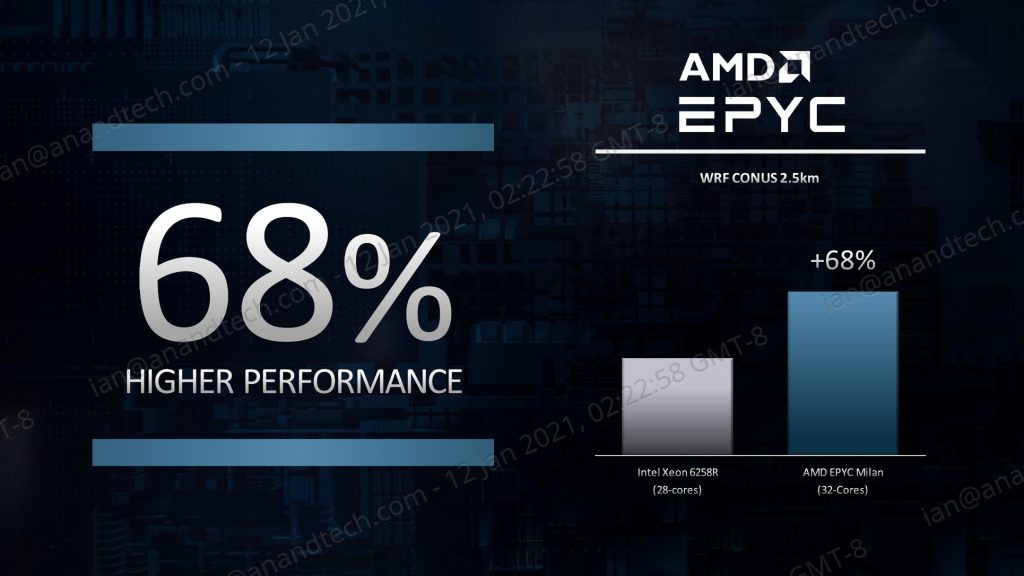
In today’s keynote presentation, AMD CEO Dr. Lisa Su showcased weather prediction simulation code known as WRF, with two of the new 32-core Milan processors up against Intel’s popular 28-core Xeon Gold 6258R. The demo showcased simulating a 6 hour weather pattern over the continental US, to which dual socket Milan was 46% faster than Intel. This was computed based on the final frame cut-away from the simulation in the keynote, which showed that where Intel was 56% complete, AMD was 82% complete.
AMD’s own metric then showed a +68% difference when comparing a single socket solution. AMD did not provide exact details on the rest of the system used in their testing. It should be clear that because this is a preview, we cannot validate AMD’s performance claims.
We are expecting more details about Milan and AMD’s portfolio later this year. Sooner rather than later.